DVI (Digital Visual Interface) is a digital video connection that was once common on computers and displays. While mainly superseded by HDMI in home theater applications, DVI can still be found on some older HDTVs, graphics cards, and video equipment.
As an AV engineer, I often had to work out how to integrate a DVI device into a system with only HDMI or analog video connections.
In this article, you’ll learn about the different types of DVI cables and connectors, the resolutions supported, and how to convert DVI to different connection types, like HDMI, VGA and DisplayPort.
Key Points
- DVI was once a standard digital video interface for PCs and displays before being primarily replaced by HDMI. It can still be found on some older hardware.
- There are 3 main DVI connector types – DVI-D (digital only), DVI-A (analog only), and DVI-I (both digital and analog). DVI-I offers the most compatibility.
- DVI supports high resolutions like 1080p but cannot carry audio signals. You need a separate audio connection.
- While HDMI has become the standard AV interface, DVI is still useful for integrating legacy video equipment without HDMI inputs. Adapters allow connectivity.
Main Topics
Introduction to DVI: The Forgotten Digital Display Interface
Developed in the late 1990s as the successor to VGA, the DVI (Digital Visual Interface) connection was designed primarily for digital video transmission between computers and monitors.
However, DVI gained little traction in home AV systems for several key reasons:
- It was introduced before the digital home theater revolution when analog inputs were still prevalent.
- Designed for PC use, DVI lacked support for audio signals and content protection features critical for consumer electronics.
- By the early 2000s, HDMI emerged as the preferred digital interface for home theater with audio, HDCP, and other enhancements tailored to AV needs.
While some early HDTVs and disc players included DVI ports, adoption was minimal compared to VGA, component video, and eventually HDMI.
HDMI completed what DVI had started – bringing fully digital AV signal transmission to home entertainment.
However, DVI enjoyed a long run as the primary PC monitor connection before eventually being displaced by HDMI. This is why DVI-to-HDMI adapters are sometimes needed to connect PCs to AV receivers and projectors.
What Does the DVI Port and Cable Look Like?
The DVI connection on your device will look something like this:

It is a standard port on modern computer graphics cards and AV devices such as projectors.
Some manufacturers will color the port depending on which type of DVI connector it is – DVI-D, DVI-A or DVI-I. See below for more information on the different types.
The cable that is used to connect two devices looks like this:
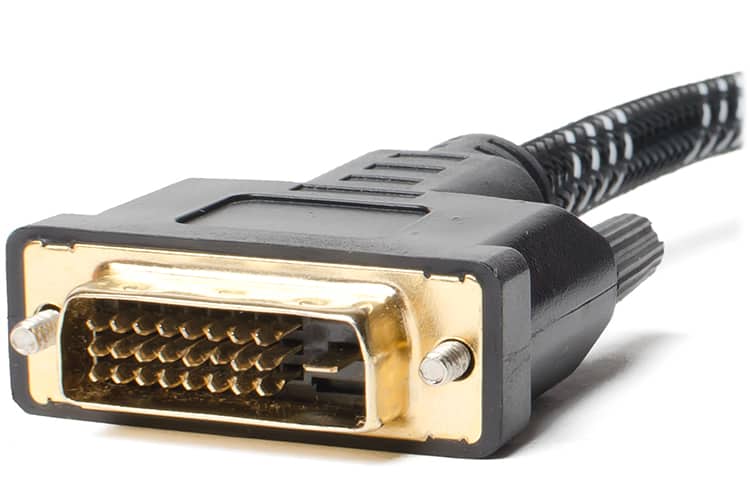

The ‘D’ shape means the video cable can only be inserted one way around.
The DVI connection on the end of the cable may have different amounts of pins depending on the type of DVI connection it is designed for. The different pin configurations are explained below.
When Should You Use DVI?
While the HDMI connection has become the standard digital AV interface, DVI ports can still be found on some older or specialty video equipment. In these cases, you should use a DVI connection if available.
What if you only have one DVI port, an input or output? In that case, you can use a converter cable or interface box to pass the video between the different connection types.
DVI can send high-quality, uncompressed digital video signals, making it preferable over analog connections like component, S-Video, and composite.
The digital signal provides a crisper image by avoiding analog distortions or interference.
| Display Mode | Single Link | Dual Link |
|---|---|---|
| SXGA (1280 x 1024) | Yes, up to 85 Hz | Yes |
| FHD (1920 x 1080) | Yes, up to 60 Hz | Yes, up to 144 Hz |
| UXGA (1600 x 1200) | Yes, up to 60 Hz | Yes |
| WUXGA (1920 x 1200) | Yes, up to 60 Hz | Yes, up to 120 Hz |
| WQXGA (2560 x 1600) | Yes, up to 30 Hz | Yes, up to 60 Hz |
| QXGA (2048 x 1536) | No | Yes, up to 72 Hz |
| WQUXGA (3840 x 2400) | No | Yes, up to 30 Hz |
| Source: Wikipedia | ||
However, unlike HDMI, DVI cables cannot carry audio data. So, using DVI means you still need a separate analog or digital audio connection between your source device and speakers or receiver.
Of course, analog connections like component, S-Video, and composite also require a separate audio connection.
DVI Connector Types
There are three main types of DVI connections and cables:
- DVI-D: Digital-only DVI that carries a digital video signal but no analog. DVI-D cables have pins for the digital TMDS data links but omit analog pins. Nearly all modern displays and GPUs use DVI-D.
- DVI-A: Analog-only DVI that carries VGA and RGB analog signals but no digital video. DVI-A was rarely used, even when DVI was more common.
- DVI-I: Integrated DVI that carries both digital video and analog RGB signals. DVI-I cables have pins for TMDS digital and analog links, providing the most backward compatibility.
DVI-I is the most versatile option, as it can connect digital video sources to either digital or analog displays. The digital signal remains crisper, but DVI-I allows legacy analog monitor support.
You can identify the DVI port type on your equipment based on the pin layout. You can see the standard connection types here:
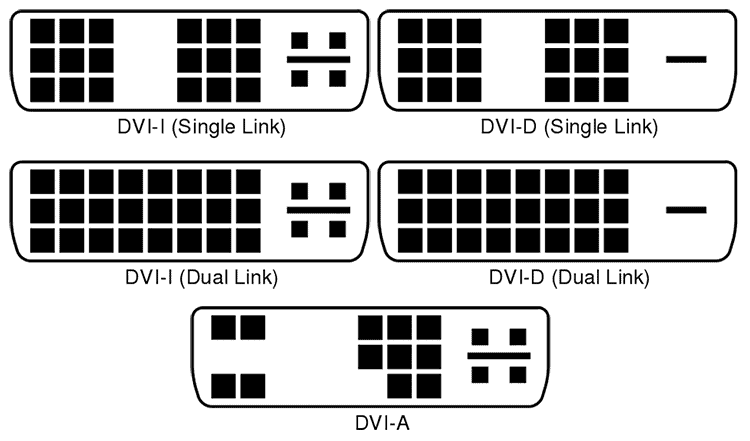
Confirming the cable type you need is best to avoid issues like connecting a digital source to an analog monitor.
Dual-Link DVI
Dual-link DVI is a less common fourth type of DVI connection, used for very high-resolution displays. It consists of two TMDS links in one connector instead of just one.
With two serialized data links, dual-link DVI doubles the available video bandwidth to over 300 MHz.
This enables DVI to support extremely high resolutions up to 2560×1600 (WQXGA) at 60 Hz refresh rates. It will even support 4K 3840×2400 (WQUXGA) at 30 Hz.
Dual-link interfaces require specialized DVI cables with additional pins to carry the extra TMDS video channels. Cables are often labeled ‘Dual-Link DVI-D,’ signifying support for the other digital data links.
However, dual-link DVI ports are rare. Most consumer devices and monitors utilize standard single-link DVI or HDMI, which can readily handle up to 1080p FHD.
Dual-link DVI is mainly found on specialized high-resolution PC monitors and graphics workstation cards.
How Does DVI Transmit Video Signals?
DVI is unique in that it can send both digital and analog video signals.
DVI uses TMDS (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling) links for digital video. TMDS encodes the video data with a high clock rate for a high throughput signal that travels through the DVI cable via twisted wire pairs.
This allows DVI to send high-quality digital video.
Single-link DVI has one TMDS link (maximum speed of 4.95 Gbps), while dual-link DVI has two links (up to 9.9 Gbps). More links mean more data and higher resolutions.
For analog video, DVI uses separate pins just for the red, green, blue, and sync signals like old VGA cables. This allows it to send the analog RGB video signal from the source to the display.
DVI-I cables include both to handle digital and analog signals.
Can You Convert DVI to HDMI?
The digital DVI-D or DVI-I version is compatible with an HDMI connection – so you can get DVI to HDMI cables or adapters if your AV equipment requires a connection like this.
Remember, a DVI connection doesn’t transfer audio signals, so these cables will send the picture but not the sound.
- For any HDMI and DVI connections, including laptops, PC's, game consoles and set-top boxes
- Sizes: 3 and 6 feet
- Supports 1080p video, from 800x600 to 1920x1200 resolution
- Bi-directional - HDMI out to DVI in, or DVI out to HDMI in
- Video only; you will need to make a separate connection for audio
The cable pictured above will work both ways.
So you can send a signal from a DVI-D output to an HDMI input – or from an HDMI output to a DVI-D input. Terrific!
Another thing to check is the image resolution supported by the cable.
The cables above support 1080p video with a maximum resolution of 1920×1200.
How Do You Connect DVI to a VGA Monitor?
There may be a time when you have a DVI output but only a VGA input on your monitor.
Do DVI to VGA adapters work? They do.
If you use the DVI-I or DVI-A versions, you can buy an adapter to convert your DVI output into a VGA interface.
Then, you just need to connect a VGA cable to your display.
- Easily convert DVI to VGA for older display
- Supports up to Full HD 1080p@60Hz
- Plug and play
- It only works with a DVI-I connection, not DVI-D. Check the manual of your output device to ensure it outputs DVI-I.
Does this work both ways? No, this adapter is designed for a DVI-I to VGA connection.
The male DVI connector plugs into your device’s female DVI output, and you connect a standard VGA cable to the female VGA connector.
Finally, simply plug this into your monitor.
DVI-D to VGA Connections
What if your device has a DVI-D output? Then you will need a different type of adapter.
This active VGA adapter will work with any DVI-D device – such as the graphics card connector of a desktop or laptop.
- Creates a VGA female connection for a standard VGA cable
- Ideal for older monitors and projectors
- Supports standard 1080p up to 1920x1200
- Plug and play - no driver required
- Not bi-directional - DVI to VGA only, not VGA to DVI
This adapter supports 1080p TV resolutions at 60Hz – up to 1920×1200 @60Hz.
How to Make VGA to DVI Connections
You have learned how to make a DVI to VGA connection, but what if you need to connect everything the other way?
In this case, you will need a different device.
If you want to make a VGA to DVI connection, you can buy an adapter like this one:
- You only need a simple DVI-A cable to wire everything together
- Gold-plated connectors
- Easy installation
- It only works with DVI-A (analog), not DVI-D (digital), so ensure your display device supports this
This VGA to DVI-A adapter lets you connect an older device with a VGA output – like a graphics card – to a DVI-A input on your display device, like a monitor or projector.
It doesn’t send audio, so you must make a separate sound connection between the source device and the speaker system.
The critical thing to check before buying is if your monitor or projector supports DVI analog.
This adapter doesn’t convert the video signal from analog to digital; it simply changes the interface from VGA to DVI.
Therefore if your display device only accepts DVI-D (digital), this won’t work.
Can You Connect DisplayPort to DVI?
Another common problem with modern AV connections is connecting DisplayPort connections to DVI.
DisplayPort is common on new graphics cards and monitors, but this can lead to problems when you have older hardware without a DP interface.
Fortunately, DisplayPort is compatible with DVI; you just need to buy the correct cable or adapter.
The main problems of DisplayPort and DVI connections are:
- DisplayPort only natively supports single-link DVI, not dual-link. However, active dual-link adapters are available, which are more expensive.
- Adapters need to change the voltage between DVI and DisplayPort, which can slow performance.
- Simple passive adapters only work from DisplayPort to DVI. You will need to buy a more expensive active adapter to send a signal in the other direction, from DVI to DisplayPort. These are less common than DisplayPort to DVI solutions.
For DisplayPort to DVI, you can buy a simple cable with DP and DVI connectors at either end.
- DisplayPort male to DVI male
- Sizes: 3, 6, 10 and 15 feet
- Supports video resolutions up to 1920x1200 @60Hz
- Gold-plated connectors
- Not bi-directional, DisplayPort to DVI only
If you need the higher resolutions of dual-link DVI, you will need to spend more and buy an active adapter that can handle the higher bandwidths.
- Supports screen resolutions up to 2560x1440 @ 60Hz
- DVD-D female connector for connecting a standard DVI cable
- Plug and play, no drivers required
- Requires power via the supplied USB connector
- It needs a dual-link DVD-D cable
While plenty of cables and adapters support sending from DisplayPort to DVI, finding solutions for sending a video signal the other way is more challenging.
Here is an active DVI-D to DisplayPort adapter cable that does work in this way:
- Supports resolutions up to 1920x1080 @60Hz
- 1.8m cable
- DVI-D single link support
- Male to male connectors, no further cables required
- USB power connector available if required
- DVI-D (digital) to DisplayPort only, not the other direction
- It doesn't work with DVI-I connections
- The adapter must connect directly to the DVI port of the source device
You must buy the correct adapter for the job, as all of these solutions are unidirectional and will only send video in one direction.
You must also check if your devices support DVI-D, DVI-I or DVI-A. This is very important with these converters as they often only work with one type.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does DVI Stand For?
DVI stands for Digital Visual Interface.
Is DVI Better Than HDMI?
DVI sends the same high-quality digital video signal as HDMI. However, unlike HDMI, DVI doesn’t support audio signals, so you must make a separate connection to hear the sound.
Are DVI and HDMI the Same?
DVI-D and HDMI are similar, although not exactly the same. The main differences are that HDMI supports stereo and multichannel audio, the YUV color space and CEC control signals – where DVI doesn’t. You may also have trouble playing copyright-protected material with DVI as the connections may not support HDCP.
What Are the Three Types of DVI Connectors?
The three types of DVI connectors are DVD-D (digital signals), DVI-A (analog signals) and DVI-I (compatible with both digital and analog).
About The Author
Paul started the Home Cinema Guide to help less-experienced users get the most out of today's audio-visual technology. He has been a sound, lighting and audio-visual engineer for around 20 years. At home, he has spent more time than is probably healthy installing, configuring, testing, de-rigging, fixing, tweaking, re-installing again (and sometimes using) various pieces of hi-fi and home cinema equipment. You can find out more here.











