HDMI is the standard for connecting audio-visual devices. It handles video and audio signals between your components. But HDMI can be confusing. This article explains common issues like:
- When to use HDMI
- Supported video and audio formats
- Different cable standards – which do you need?
If you’ve ever had a question about HDMI, this comprehensive guide will answer these questions and more.
Main Topics
HDMI Basics
In this section
- What is HDMI?
- What Does the HDMI Connector Look Like?
- What Does the HDMI Cable Look Like?
- What Are the Different Versions of HDMI?
- Are the New Versions of HDMI Compatible With the Old Versions?
- Can You Upgrade Your TV or AVR from HDMI 2.0 to HDMI 2.1 with a Firmware Update?
- What Are the Different Types of HDMI Connectors?
- HDMI Pin Out Layouts
- What Is the Difference Between HDMI and DVI?
What is HDMI?
HDMI is the go-to connector for sending high-quality video and audio between your TV, receiver, game console, Blu-ray player, and other home entertainment devices.
What makes HDMI so great? A few things:
- Video: It supports all the latest video formats like 4K, 8K, HDR, and high frame rates up to 120fps. No more juggling component cables for video – HDMI handles it all over a single cable.
- Audio: It carries multi-channel surround sound like Dolby Atmos that older connections can’t. HDMI keeps quality high for both your video and audio.
- Versions: There have been several versions of HDMI, each with its own capabilities. The latest HDMI 2.1 has the bandwidth for 8K video and new gaming features.
- Limitations: Older HDMI versions have limits, so it helps to know what version your TV, console, etc. are rocking. The connector may look the same, but performance can vary.
The bottom line: HDMI delivers great high-res video and audio, making it the first choice for home theater hookups. Look for HDMI 2.1 if you want the newest, future-proofed features.
What Does the HDMI Connector Look Like?
The HDMI connector on the back of your TV or Blu-ray player looks like this:

The HDMI connector has a distinctive rectangular shape that fits cables one way. Ports are usually inputs or outputs:
- HDMI input: receives signals, like a TV
- HDMI output: sends signals, like a Blu-ray player
- HDMI input/output: does both, like an HDMI ARC port on a TV
Understanding if a device sends or receives signals makes wiring easier. So think about this the next you are stuck looking at your AV system, wondering where all the wires go!
What Does the HDMI Cable Look Like?
The HDMI cable that is used to connect two devices looks like this:
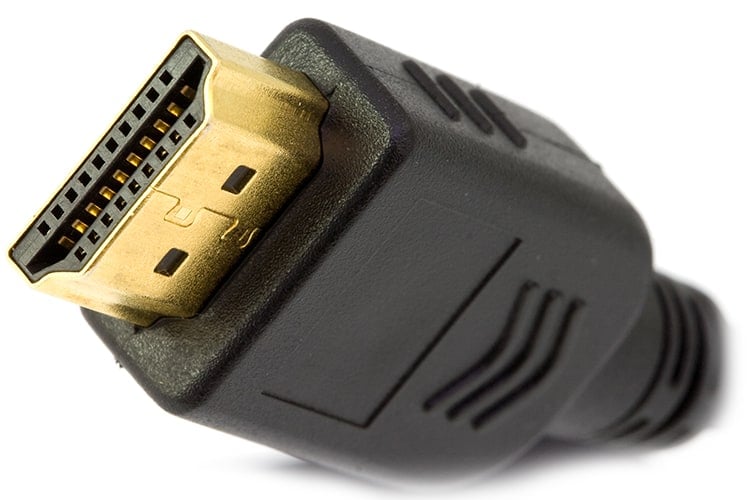

HDMI cables have a distinctive shape, meaning you can only plug them in one way around. A single cable transfers both sound and picture between devices.
Key features:
- The rectangular connectors are usually silver, but some are gold-plated. The material used will have no impact on performance.
- A flexible plastic covering protects the inner wiring.
- Some wires use braided nylon for easier installation or aesthetics.
- There is no difference in performance based on connector color/material.
The cable’s job is to transfer audio/video signals between HDMI ports. Even cheap, well-made cables will do this with no issues.
The shape and inner wiring matter most, not minor variations in outer appearance.
What Are the Different Versions of HDMI?
HDMI 1.0
- The release version of the HDMI standard – an audio and video interface that allowed the transfer of standard and high-definition video.
- Up to 8 channels of uncompressed digital audio.
- Data transfer up to 4.9 Gb per second.
- Playback of standard Blu-ray disc video and audio at full resolution.
HDMI 1.1
- Added support for DVD Audio.
HDMI 1.2 and 1.2a
- Support for the One Bit Audio format such as SACD (up to 8 channels).
- Fully specified support for Consumer Electronics Control (CEC).
HDMI 1.3
- Increased bandwidth to 10.2 Gb per second.
- Improved color – support for Deep Colour and x.v.Colour. These provide increased color depths and the ability to reproduce any color the eye can see.
- Lip sync – allows devices to automatically synchronize the picture and sound.
- CEC extensions for controlling consumer electronic devices.
- Support for streaming high-definition Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio to an AV receiver for decoding.
- Defined two standards for HDMI cables – category 1 and 2 (see below).
HDMI 1.4
- Support for increased resolutions – up to 3840 x 2160p at 25/30Hz and 4096 x 2160p at 24Hz.
- Support for the audio return channel (ARC). Allows the TV to send audio from an HDMI connection to an AV receiver or soundbar. Therefore allowing an easy way to send this audio to a home theater sound system.
- Allowed for an Ethernet connection over HDMI – therefore allowing an internet or home network connection through the cables.
- Support for 3D TV signals.
HDMI 2.0
- Supported bandwidth increased to 18Gb per second.
- Added support for 4K Ultra HD resolutions at 60 frames per second.
- Support for the BT.2020 standard for UHD TVs.
- Support for up to 32 audio channels.
- Support for up to 1536 kHz audio resolution.
- Support for dual video streams to the same screen.
- Added support for 21:9 aspect ratios.
- The minimum standard required for HDCP 2.2 (copy protection for 4K video). However, if a device is HDMI 2.0, it doesn’t necessarily mean it supports HDCP 2.2. Unless there is HDCP 2.2 through the whole playback chain, then 4K video won’t play.
- No need for a new cable; just use a category 1 or 2 cable.
HDMI 2.0a
- Added support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) video.
HDMI 2.0b
- Added support for Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG) video – a form of HDR.
HDMI 2.1
- Added support for Dynamic HDR
- Support for 4K/120 and 8K/120 video resolutions
- Support for Display Stream Compression (DSC). This allows for Type A (uncompressed) and Type B (compressed) video
- Specified a new cable type – 48G. This supports a bandwidth of 46 Gb/s and uses HDMI type A (standard), C (mini) and D (micro) connectors
- Specified a new Enhanced Audio Return Channel (eARC). Allows the transfer of uncompressed and object-based audio from the TV to a home theater system via an existing HDMI connection. eARC also supports a new Auto Lip Sync feature.
- Support for enhanced gaming and media features such as:
- Variable Refresh Rate (VRR): allows the refresh rate of the screen to change to match how quickly the player can produce the content. This reduces lag and stutter during gaming. All devices in the chain need to support this.
- Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM): when compatible devices are connected, they will automatically switch to their gaming modes. This means that they enable their best low latency settings for gaming. All devices in the chain need to support this.
- Quick Media Switching (QMS): removes any delay before content is displayed. For example, you may get a temporary black screen when you switch from one video source to another – especially if you are switching video resolutions or frame rates. QMS stops this black screen from happening. All devices in the chain need to support this.
- Quick Frame Transport (QFT): allows the source device to send video frames to the TV as soon as they are produced – rather than wait until the display device is ready for it. This reduces latency when gaming. All devices in the chain need to support this.
Are the New Versions of HDMI Compatible With the Old Versions?
Yes. HDMI is fully backward compatible with older versions.
Can You Upgrade Your TV or AVR from HDMI 2.0 to HDMI 2.1 with a Firmware Update?
No. The circuitry in an HDMI 2.1 board uses the wiring inside an HDMI cable differently. So you would need a new HDMI board installed inside your device.
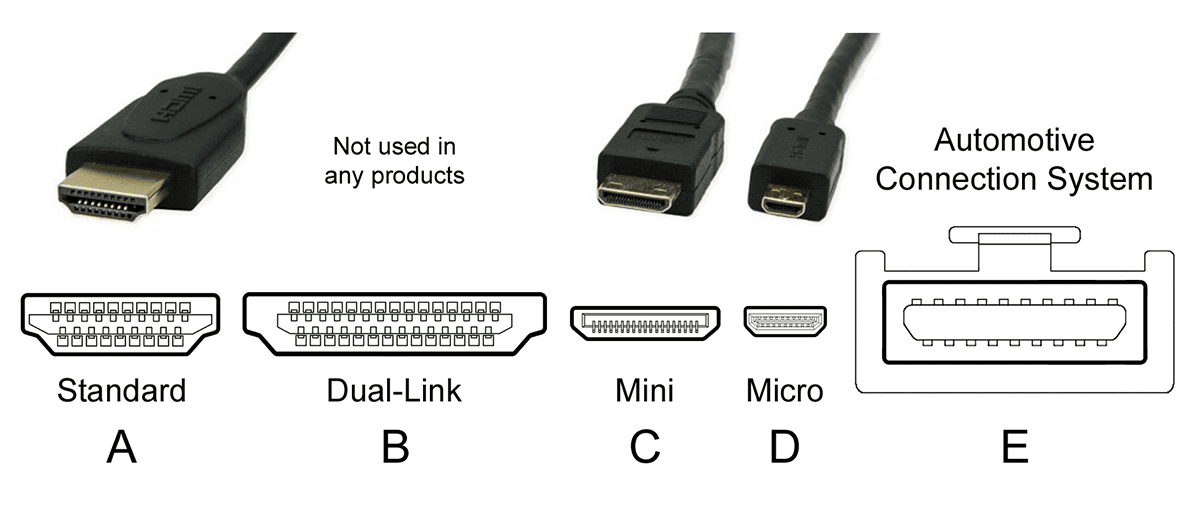
What Are the Different Types of HDMI Connectors?
There are five types of HDMI connectors:
Type A
- Standard Connector
- Defined in the HDMI 1.0 specification
- 13.9 mm x 4.45 mm
- 19 pins
- Compatible with single-link DVI-D
Type B
- Dual-Link Connector
- Defined in the HDMI 1.0 specification
- 21.2 mm x 4.45 mm
- 29 pins
- Compatible with dual-link DVI-D
- Not used in any products
Type C
- Mini Connector
- Defined in the HDMI 1.3 specification
- 10.42 mm x 2.42 mm
- 19 pins
- Designed for portable products
- Can be connected to type A with a converter cable
Type D
- Micro Connector
- Defined in the HDMI 1.4 specification
- 5.83 mm x 2.2 mm
- 19 pins
Type E
- Automotive Connection System
- Defined in the HDMI 1.4 specification
- Has a locking tab to keep it in place
- There is an adapter for connecting to the other types
HDMI Pin Out Layouts
Standard type A HDMI cables have 19-pin connectors that transfer data between devices.
The HDMI specification defines each pin for a specific task. In the earlier HDMI versions, some pins were optional or reserved for future use.
For example, pin 14 was reserved in HDMI 1.0-1.3a but is used in HDMI 1.4+ for the Ethernet and audio return channels.
There are four shielded twisted pairs for sending video and audio data, with seven more conductors used for features like the Display Data Channel, CEC, Audio Return Channel and power.
Three of the seven separate conductors in an HDMI with Ethernet cable also form an extra twisted pair.
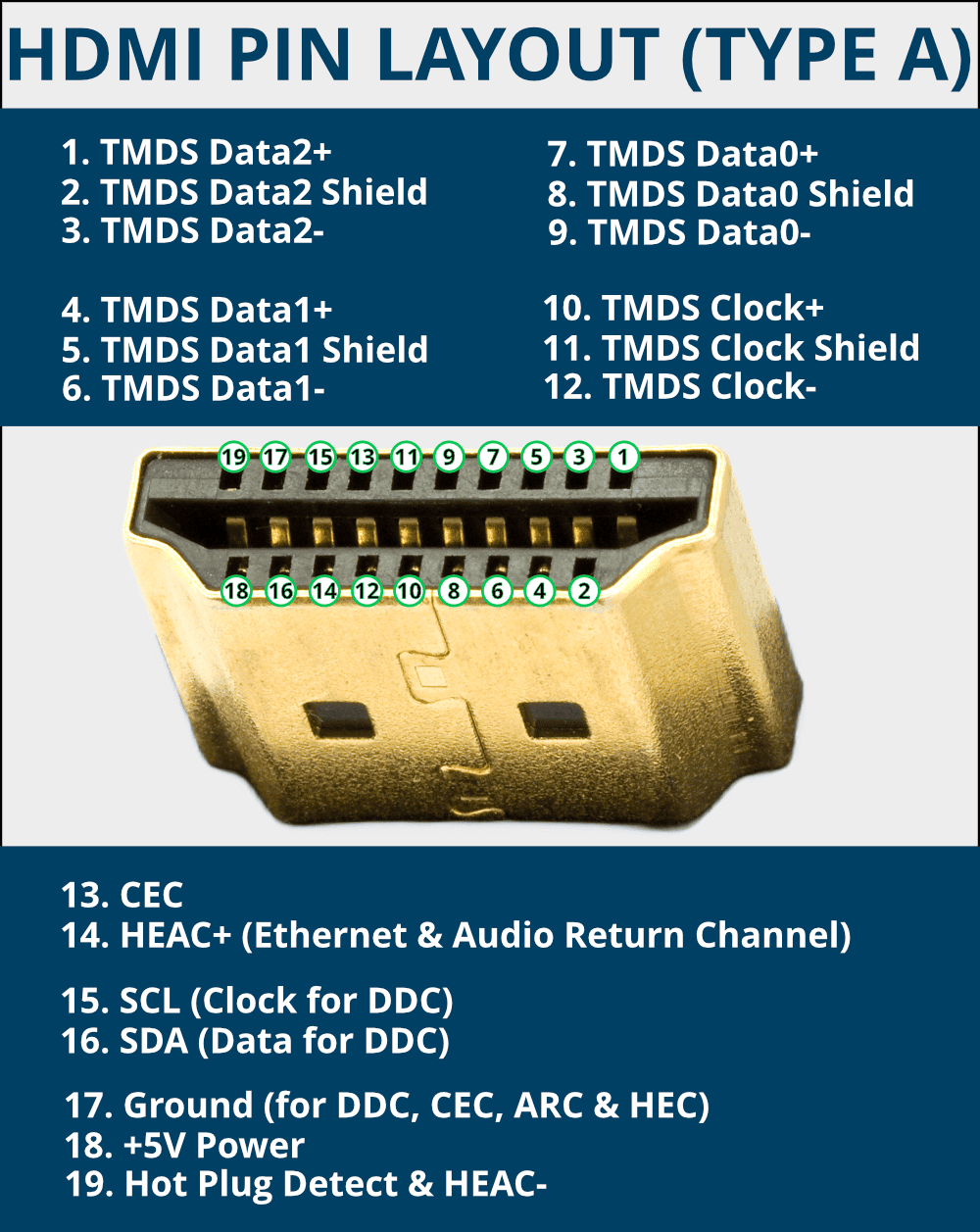
The main types of communication within HDMI are:
- TMDS: HDMI uses transition-minimized differential signaling (TMDS) to send video, audio and auxiliary data between devices.
- CEC: consumer electronics control allows you to control several devices connected via HDMI with a single remote – such as volume and power commands.
- DDC: the display data channel sends EDID data between devices to communicate which media formats and display modes they support.
- ARC and HEC: HDMI Ethernet and Audio Return Channel (HEAC) were introduced in HDMI 1.4. HEC is a high-speed two-way data link for video, audio, data and Ethernet communication. ARC allows HDMI connections to send audio information back to the source for playback, e.g., a TV can send audio to an AV receiver to hear on a surround sound speaker system.
Type C Mini HDMI connectors also have 19 pins. However, some of the pins are assigned in a different order, so you can buy a type A-to-C HDMI cable if you need to mix and match connectors.
The Micro HDMI Type D connector also has 19 pins, but the assignment for each pin differs from both type A and C cables.
What Is the Difference Between HDMI and DVI?
Broadly, HDMI and DVI are the same. The main difference is HDMI has support for 8 channels of audio, support for the YUV color space, CEC (wiring to enable remote control of devices) and a different connector.
HDMI Audio/Video Support
In this section
What Audio Formats Does HDMI Support?
Any device with HDMI must support the minimum standard of uncompressed stereo LPCM audio.
Any other formats are optional, so the audio types available to you will be limited by the hardware you use.
- HDMI allows for:
- 8 channels of compressed and uncompressed audio
- At 1-bit, 16-bit, 20-bit and 24-bit
- At sample rates of 32kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz, 96 kHz, 176.4 kHz and 192 kHz
- Support for 32 channels of audio was introduced in HDMI 2.0
In practice, you will have access to all popular modern audio formats.
HDMI supports all the common stereo and multichannel audio formats for modern TV, movie and music content:
- LPCM (2-ch to 8-ch)
- Dolby Digital
- Dolby Digital Plus
- Dolby TrueHD (since version 1.3)
- Dolby Atmos
- DTS
- DTS-ES
- DTS 96/24
- DTS Express
- DTS-HD High Resolution
- DTS-HD Master Audio (since version 1.3)
- DTS:X
- DVD-A (since version 1.1)
- DSD (since version 1.2)
Many other audio formats, such as FLAC, ALAC, and WAV, will also be available if supported by your hardware.
If you need something specific, you should check that device’s documentation. It won’t be HDMI limiting you; it will be the design of your device.
All HDMI cable types will support transferring all audio formats within the specification. If you are unsure, the guide to surround sound formats explains all about Dolby and DTS audio.
What Video Formats Does HDMI Support?
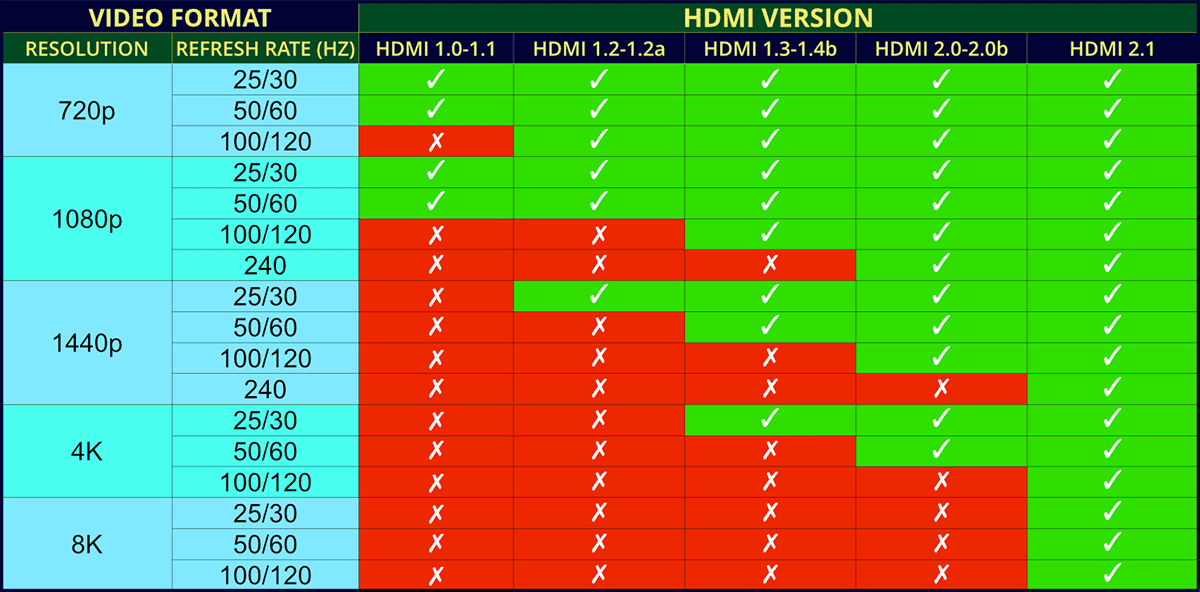
Source: Wikipedia & HDMI.org
As the HDMI specification is updated, more video formats are supported. Your hardware must support the HDMI version to use a specific video resolution.
Remember, manufacturers may still limit some video formats on their devices. They may also add support for a format that isn’t in the HDMI specification – as long as it is within the bandwidth limits of that version.
Always check the manual for your device to see what it can do.
If you are unsure what the video formats mean, see the guide to TV resolutions or what is the refresh rate of your TV?
HDMI 1.0-1.1 Video Formats
- 720p@25/30/50/60Hz
- 1080p@25/30/50/60Hz
HDMI 1.2-1.2a Video Formats
- 720p@100/120Hz
- 1440p@25/30Hz
HDMI 1.3-1.4b Video Formats
- 1080p@100/120Hz
- 1440p@50/60Hz
- 4K@25/30Hz
HDMI 2.0-2.0b Video Formats
- 1080p@240Hz
- 1440p@100/120Hz
- 4K@50/60Hz
- 5K@25/30Hz
HDMI 2.1 Video Formats
- 1440p@240Hz
- 4K@100/120Hz
- 5K@50/60/100/120Hz
- 8K@50/60/100/120Hz
- 10K@50/60/100/120Hz
Do You Need an HDMI 1.3 Device to Hear HD Audio?
You do not need an HDMI 1.3 device to hear high-definition audio. Earlier HDMI versions could transfer HD audio too, just in a different way.
Before HDMI 1.3, the playback device would decode HD audio into a Linear PCM signal. The source device would then send the signal over HDMI to an amplifier that supported HDMI audio.
HDMI 1.3 added the ability to bitstream HD audio instead. With bitstreaming, the raw HD audio data is sent directly to the amplifier without decoding first. The amplifier then decodes the signal.
Bitstreaming requires all devices to be HDMI 1.3 compliant.
Choosing HDMI Cables
In this section
How to Choose the Best HDMI Cable
When you are looking to buy a new cable, there are endless variations to choose from.
There are different colors, lengths, materials, specifications, and prices. It can make your head spin.
Fortunately, it’s not too tricky once you concentrate on the important stuff.
Think about these points to find the best HDMI cable for you:
- Check the specification: Most people need a category 2 high-speed HDMI cable these days. Category 2 will ensure that the cable has been certified to transmit data up to 4K resolutions – and all current audio formats. If you want to run the highest rates at 8K, you might need an Ultra High-Speed HDMI cable.
- Materials: Most cables have a standard protective PVC plastic exterior and shielding to prevent signal interference. Some brands will come with a nylon braided cord, making the cable more flexible and easier to move in tight spaces. Otherwise, it just makes it looks nice. It shouldn’t matter either way for most people, but a more flexible and smaller cable may ease installation.
- Price: You can break the bank and buy a costly one if you like. However, it won’t perform any better than a good-quality budget cable. The AmazonBasics range will probably be sufficient – or if you want a braided model, then these Twisted Veins HDMI cables are popular.
- Length: Very important. Please take a few seconds to think about where the cable will need to run and how far that will be. As a rule of thumb, the shorter, the better – as really long wires can negatively affect the signal. Running the cable in a confined area might be tricky if you get one too long. Get one too short and…
- Color: That’s up to you – it won’t make much difference to the sound and picture! Some people will go for a discreet color that can be easily camouflaged among their equipment. Most will just get a black one!
What Is the Maximum Cable Length for HDMI?
There’s no set maximum length for HDMI cables – it’s about how well the cable transfers the signal. Quality matters more than distance.
A good HDMI cable can reliably go about 10 meters (33 ft). After that, you may need a signal booster.
Short cables, like under 3 meters (10 ft), are no problem for pretty much any decent cable.
The takeaway? Don’t waste money on fancy cables if you only need a short connection. Build quality matters more than the price for longer cables. Focus on getting a cable that works well at the distance you need.
What Are the Different Speeds of HDMI Cable?
Be careful when you are buying an HDMI cable. Some brands like to make out that their cable is faster than the rest and use many exciting ways to describe them.
There are currently only three official specifications for the speed of an HDMI cable:
- Category 1: Standard Speed – tested up to 2.2 Gb per second.
- Category 2: High Speed – tested up to 10.2 Gb per second.
- Category 3: Ultra High Speed – tested up to 48 Gb per second.
Categories 1 and 2 have two different types of cable – an ordinary cable and one ‘with Ethernet.’
Internally, HDMI cables have 4 shielded twisted pairs and 7 separate wires. The ‘with Ethernet’ versions use two of the 7 individual wires to create an extra twisted pair conductor.
A Category 3 HDMI cable includes the Ethernet wiring as standard.
Category 1 HDMI Cables
A ‘standard speed’ category 1 cable has been tested at speeds of 75 MHz.
An HDMI cable has 3 data pairs of wire that transmit the signal, and the two different categories of HDMI cable are speed tested using just one data pair.
Yet the bit rate you see quoted will often be the combined total for all three – to get a higher number to impress you with.
This means a ‘standard speed’ category 1 cable has been tested to transfer data at 742 Mb per second for a single data pair – or 2.2 Gb per second for the three combined. This is the equivalent of a 720p or 1080i video signal.
Category 2 HDMI Cables
A ‘high speed’ cable that has been tested at speeds of 340 MHz.
This is up to 3.4 Gb per second for each data pair – or a maximum of 10.2 Gb per second for three pairs combined.
This is the equivalent of a 1080p signal at 60 frames per second – or a 4K 2160p signal at 30 frames per second – including 3D video and any signals with increased color depth.
There is a new certification for a ‘Premium High-Speed HDMI Cable.’ This is a category 2 cable tested up to the theoretical maximum of 18 Gb per second – and should support any video up to 2160p/60Hz, BT.2020 and HDR.
However, in reality, any ‘high-speed’ HDMI cable will probably work fine.
Category 3 HDMI Cables
This is an Ultra High-Speed HDMI Cable tested at data transfer rates up to 48 Gb/s. This new category was introduced to allow for the increased speed requirements of the HDMI 2.1 specification.
This includes video resolutions of 4K and 8K at 120 frames per second. The full range of video resolutions and frame rates supported by HDMI 2.1 and an Ultra High-Speed Cable are:
- 4K@50/60/100/120p
- 5K@50/60/100/120p
- 8K@50/60/100/120p
- 10K@50/60/100/120p
It will also handle the high-resolution audio formats required for eARC – Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, Dolby Atmos and DTS:X.
However, any HDMI cable supports these audio formats, so you don’t need to buy one of these cables just for high-resolution audio. A category 3 cable will work with any older HDMI connection types.
What Is an HDMI with Ethernet Cable?
Category 1 and 2 cables come in two types – standard and’ with Ethernet.’ Compared to an ordinary HDMI cable, an HDMI with Ethernet cable has an extra twisted pair of wires inside.
Category 3 cables come with the Ethernet wiring as standard. HDMI eARC connections require a ‘with Ethernet’ cable.
What Is an Ultra High-Speed HDMI Cable?
Ultra High-Speed HDMI cables are a new cable type released for the HDMI 2.1 specification, and they are category 3 cables. Initially called 48G cables, an Ultra High-Speed HDMI cable supports data rates up to 48 Gbps.
The increased speed is required to support the new features of HDMI 2.1 – uncompressed 8K/60p, 4K/120p and high-resolution audio via eARC. It is fully backward-compatible with older HDMI connections.
Do You Need a Gold-plated HDMI Cable?
No, you don’t need to buy an HDMI cable with a gold-plated connector.
The theory is that a gold-plated connector will be more resistant to oxidization and better conduct the signal.
The truth is you are hardly likely to get much oxidization going on in your living room. Or is your TV in the garden?
Anyhow, there is such a small amount of gold in the gold plating that it won’t make much difference anyway. Still, it looks nice and shiny.
By all means, buy an HDMI cable with gold-plated connectors, but you really don’t need to pay extra just for this feature.
Where Can You Buy an HDMI 1.4 or HDMI 2.0 Cable?
Cables aren’t defined by the version numbers of the HDMI specification, i.e., 1.2 or 2.0.
These numbers refer to the capabilities of the HDMI circuit boards inside your devices. So, an HDMI 2.0 cable doesn’t exist.
There are currently 3 standards of HDMI cable – category 1 (standard), category 2 (high-speed and premium high-speed) and category 3 (ultra high-speed).
The different standards of HDMI cables are simply designed and tested to transfer a maximum amount of data – and higher video resolutions have required improved data rates in newer HDMI cables.
To transfer 4K Ultra HD video, 1080p video and 3D TV signals, you should make sure you buy a category 2 ‘high speed’ cable. This will ensure it will transfer the high data rates required.
If you aren’t sending the higher resolution signals, then a standard category 1 cable should be sufficient.
But you might need a category 3 ultra high-speed HDMI cable if you want to run 4K/8K video at high frame rates.
HDMI Cables for Specific Uses
In this section
Do You Need to Buy a New Cable for a 3D TV?
No, you probably don’t need to buy a new HDMI cable for 3D TV.
If you already have a ‘high speed’ category 2 HDMI cable, this will support all the requirements of HDMI 1.4 and 3DTV signals (with one exception – see below).
A standard category 1 cable hasn’t been tested to support the higher data rates and may not be reliable enough. However, before you buy a new cable, give it a try, and you may find it will work.
One part of the new HDMI 1.4 specification will require a new cable.
The 1.4 update supports an Ethernet connection through HDMI, and to utilize this in your equipment, you will need a category 1 or 2 HDMI cable ‘with Ethernet.’
Do You Need to Buy a New Cable to Watch 4K UHD Video?
You will only need to buy a new cable to watch 4K UHD video if you currently have a category 1 HDMI cable. A category 2 ‘high speed’ HDMI cable will support up to 4K/60 UHD video.
Although only ‘Premium High-Speed HDMI cables’ are tested up to the required limit, any category 2 cable should be fine.
Try your existing cables first, and if you have a problem, you can buy new ones. The cables pictured below are certified Premium High-Speed HDMI cables:
- Tested to work with 4K/60Hz video
- Available lengths: 3, 6, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 feet
- Also supports high-resolution audio like Dolby TrueHD audio
- Your old cable may work with 4K/60Hz video, even if it isn't a tested 'Premium' cable
Do You Need to Buy a New Cable for HDMI 2.0?
You might to buy a new cable for HDMI 2.0, but probably not.
An interesting point has been reached where the maximum data rate specification of the HDMI 2.0 specification has overtaken the ‘fastest’ HDMI cable.
HDMI 2.0 devices are designed to transfer data up to 18 Gb per second, whereas a ‘high speed’ category 2 cable is only intended to support a maximum of 10.2 Gb per second.
However, a well-made category 2 cable will probably handle higher data rates than tested.
To be sure, the HDMI licensing authority has introduced an optional ‘Premium HDMI Cable’ certification, which is allowed for category 2 cables that have been tested up to 18 Gb per second.
The same rule applies to that mentioned above. Try the cable you have already, and if you get picture drop-outs or interference, then maybe consider getting a ‘Premium HDMI Cable.’
Do You Need a New Cable for HDMI 2.1?
You might need a new cable for HDMI 2.1, which allows for increased video resolutions of 4K/120p and 8K/60p.
If you are trying to use any of these new video resolutions, then you may need to buy a new ultra high-speed HDMI cable:
- Tested for data rates up to 48 Gbps
- Available lengths: 1.5, 3, 5, 6.5 and 10 feet
- Braided jacket for flexible installation
- Good value
- Not available in extremely short lengths
If you are using HDMI 2.1 but not trying to transfer these new video formats, then an older Category 2 cable should be fine.
First, try your old cables; they may work. But, if you have a problem, you might need to invest in new wires. The length of your cables is significant.
If your cables are 2 or 3 meters, you might not have a problem with an older cable. But for longer distances, then the cable specification becomes more critical.
Converting HDMI
In this section
Can You Connect HDMI to VGA with a Cable?
Yes, you can connect HDMI to VGA with a single cable.
To do this, you will need to buy an adapter to convert the HDMI output to VGA – and then use a standard VGA cable to your display device.
For example, if you have a device with an HDMI output, like a laptop, you may need to connect it to a projector with only a VGA input. On the face of it, you’re a little bit stuck.
However, thanks to the wonders of modern science, there’s a relatively easy solution to the problem.
Several HDMI to VGA converters are available that will accept an HDMI signal and output it as VGA.
- HDMI male to VGA female
- Supports 1920x1080@60Hz (1080p Full HD)
- Also supports 720p, 1280x1024 and 1600x1200
- Works with laptops, Chromebooks, Roku, Wii U and many more
- Doesn't support Blu-ray players and low-power HDMI ports
All you need to do is plug the HDMI connector into the HDMI output of your laptop – or whatever device you need to send the signal from.
Then, connect the VGA to your display device – like a projector, computer monitor or TV.
The model above supports resolutions up to 1920×1080 at 60Hz and has a 3.5 mm analog audio output to extract the sound and picture.
It also comes with an external power supply that you might need if you connect to a device that doesn’t output enough power – like the Sony PS4 and Apple MacBook Pro.
These converters won’t work with devices with HDCP copyright protection, such as Blu-ray players.
Can You Buy a USB to HDMI Cable?
Sort of. You will need to buy an adapter that supports the device you are using.
So, you would convert the connection type from USB to HDMI using the adapter and then use a standard HDMI cable to connect to your display device. Why might you want to do this?
The most common reason would be that you want to connect your computer or notebook to an external monitor or HDTV – and you will then be able to send video and audio into an HDMI port on your display device.
If your device already has an HDMI output, you should just use that.
However, if you don’t have an HDMI output, you can send video and audio to another screen using a USB adapter.
You could also use this adapter to add a second monitor if you already use the HDMI output.
This USB to HDMI adapter will convert a standard-size USB 3.0/2.0 connection to 1080p video and HD audio.
- Compatible with Windows XP, 7, 8, 10 and 11
- USB 3.0 connection: up to 1920x1080@60Hz Full HD
- USB 2.0 connection: up to 800x600@60Hz
- Supports audio with USB 3.0
- Windows-only doesn't work with Macs.
- Not suitable for fast-moving images, like movies or gaming
However, this model will only work on a device running a Windows OS – XP, 7, 8, or 10 – and it also only supports 1080p video on a USB 3.0 port.
So, you must read the description of the adapter before buying one.
Many will only support specific operating systems, video resolutions, and audio formats.
If you want a USB converter that works with a Mac device – like a MacBook or iMac – then you can buy something like this QGeeM USB C to HDMI Adapter:
- Works with most USB C device like MacBook Pro, Microsoft Surface and Samsung Galaxy
- Supports resolutions up to 4K@30Hz (3840 x 2160)
- No driver software required
- Not all USB C devices will work - must be USB-C 3.1 or Thunderbolt 3 ports
This converter uses the smaller USB Type-C connection, which can be used with devices that don’t have standard USB ports.
You can also use this converter on devices such as a Surface Book, Samsung Galaxy phone, Chromebook, or Pixelbook. Anything that uses a USB Type-C connection. It is also Thunderbolt 3 compatible.
The main thing to be aware of is that USB to HDMI converters are often specific to different device types, so make sure that you buy the right one for your device.
Can You Convert a Component Video Output to HDMI?
Yes, you can convert a component video output to HDMI.
One way is to use your AV receiver. Many AV receivers can upconvert a component input to an HDMI output.
However, you will need to check the manual for the AV receiver, as not all of them will do this. If not, another way is to use an adapter or converter.
There are plenty to choose from, and the Portta component to HDMI converter, pictured below, will do the job.
- Supports HDMI 1.3
- Component input formats: 4080i/p, 576i/p, 720p, 1080i/p
- Supports uncompressed stereo LPCM audio
- 5-year warranty
- Not bi-directional - for component to HDMI only
You just need to check that the converter you use will deliver the signal you need – the one above supports resolutions up to 1080p.
Also, you need to be clear about what you want to convert from and to.
The converter above will only convert from component video (plus stereo audio) to HDMI, i.e., sending a picture from an old game console to the HDMI input on a TV.
If you need to do something different, you need to look for the correct converter for that job. This is something that many people get wrong and buy the wrong device.
What are HDMI ARC and eARC?
ARC, or Audio Return Channel, is a feature introduced in the HDMI 1.4 specification that allows a device to send data in two directions – video and audio from the source device and audio back to the source.
The main purpose of ARC is to reduce the number of cables required between devices.
In a standard HDMI connection, you can send data from a playback device to a display device.
However, with an ARC connection, you can send audio back down the same HDMI cable allowing home theater speaker systems to play sound from TV apps like Netflix or Amazon Prime easily.

HDMI ARC supports stereo PCM and compressed 5.1 audio such as Dolby Digital, Dolby Digital Plus and DTS.
HDMI eARC (enhanced Audio Return Channel) is an improvement over ARC.
It was introduced in the HDMI 2.1 specification and allows for higher bandwidth and better audio quality compared to ARC.
Here are some key points about HDMI eARC compared to ARC:
- Supports higher bandwidth and can transmit up to 192 kHz, 24-bit audio signals.
- Can transmit advanced audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio.
- Provides improved lip-sync performance.
- Supports auto-detection of connected devices and can automatically switch to the correct input/output settings.
If you prefer watching videos, here’s a simple summary of the difference between HDMI ARC and eARC:
For more detail, check out what is HDMI ARC and eARC.
Is HDMI ARC Better than Optical?
If you want to send audio from your TV to an AV receiver or soundbar, you will often have a choice of two options – HDMI ARC or a digital optical output.
So, which is best? In most cases, neither.
Does the same audio signal sound different over HDMI ARC and optical? No. However, as always, you will find some swear blind that they do.
Primarily, your circumstances will determine which one is better for your system.
Here are some differences between HDMI ARC and optical connections:
- Using HDMI ARC will save you from installing an extra optical cable if you use an AV receiver.
- HDMI ARC and optical connections both support uncompressed PCM stereo and compressed multichannel 5.1 Dolby Digital and DTS audio. However, HDMI ARC also supports Dolby Digital Plus, which optical doesn’t. HDMI eARC adds support for high-resolution audio formats like DTS-HD Master Audio and Dolby TrueHD – and object-based Dolby Atmos and DTS:X.
- Your TV and amplifier/soundbar both need to support HDMI ARC. If not, then you might need to use an optical connection instead.
- To use HDMI ARC, you will often need to enable HDMI CEC on your devices. This allows your two devices to talk to each other and automatically detect when a signal is present. Mainly this works well. However, different brands can sometimes struggle to talk to each other. If you have a problem with this, an optical connection may cause fewer headaches!
Make the decision depending on your hardware and what makes sense for your system.
In many setups, you might not have a choice; you will just use the connection type supported by all your hardware.
But if you can use either, you would usually use HDMI ARC – as it saves you from connecting another cable.
Here is a helpful table that compares the differences between optical, HDMI ARC and HDMI eARC connections:
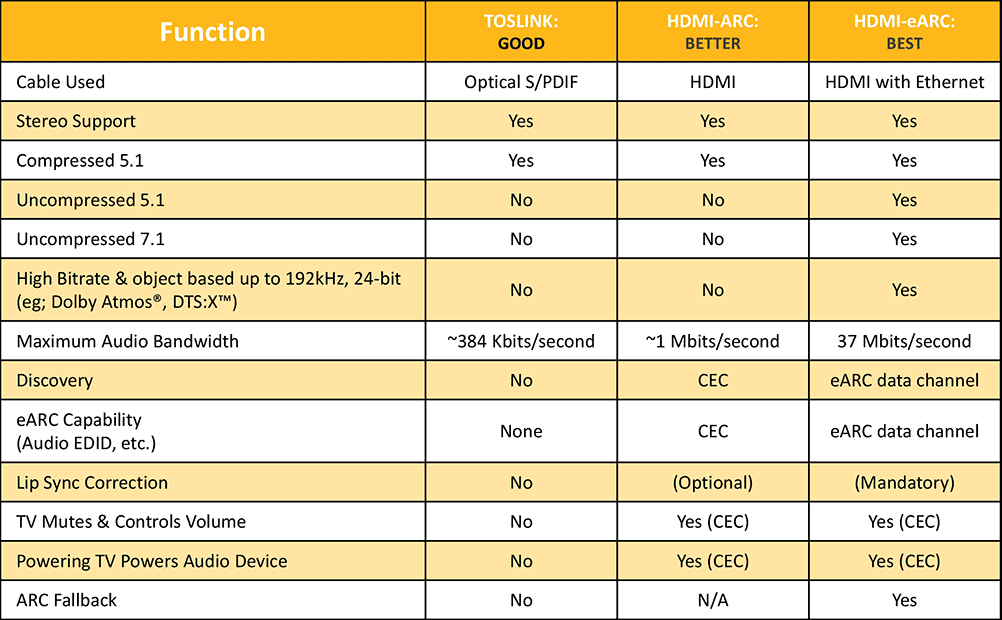
Source: HDMI.org
What is Display Screen Compression (DSC)?
The HDMI 2.1 specification allows for two types of video encoding: Type A and Type B.
- Type A: uncompressed lossless video at 4K/100, 4K/120, 8K/50 and 8K/60
- Type B: uses DSC for compressed lossy video at 4K/100, 4K/120, 8K/50 and 8K/60
Therefore, the content is compressed with Type B video using Display Stream Compression (DSC).
The lossy DSC version’s objective is to reduce the bitrate and avoid display issues with long cables.
Therefore, if an HDMI port claims to support 8K video, you might want to also check that this is for uncompressed Type A video – and not just the lossy Type B version.
An 8K port that supports both versions will be labeled 8K/60AB – whereas an 8K port with only Type B support will be displayed as 8K/60B.
What is HDMI CEC?
CEC stands for Consumer Electronics Control. CEC was fully specified in HDMI version 1.2 and allowed devices to control each other via an HDMI connection.
For example, when you switch on your TV, CEC will automatically turn on your soundbar – or your Blu-ray player will automatically select the correct HDMI input on your TV.
You will need to enable CEC in the settings menu of each device that you want to use this with.
CEC is called different things by hardware manufacturers:
- Samsung: Anynet+
- Roku: 1-Touch Play
- Sony: BRAVIA Link
- Pioneer: Kuro Link
- LG: SimpLink
- Panasonic: VIERA Link
You may find some devices, especially from different brands, might have trouble talking to each other successfully.
Also, it can sometimes be annoying as a device will switch itself on/off when you don’t want it to.
However, it can prove a useful feature when set up correctly and means you need to use fewer remote controls.
- Learn more: What is HDMI-CEC, Anynet+ & SimpLink?
Is HDMI Compatible With DVI?
Yes, HDMI is compatible with DVI – although not DVI-A.
There may be situations where you can’t just use HDMI to connect all your devices. For example, you may have HDMI on one device and a DVI connector on another.
In this situation, it is possible to buy DVI to HDMI adapters to change one end of a cable from one connector type to another.
Therefore, you can use a standard HDMI cable, put the adapter on one end, and plug the adapter into the DVI connection. Bingo!
- Bi-directional - HDMI to DVI or DVI to HDMI
- HDMI female to DVI male connection
- Up to 1080p display resolution
- Two adapters in a pack
- You must buy the necessary cables too
- No support for audio
This adapter is also bi-directional, which means you can use it to send from an HDMI to DVI connection – or from DVI to HDMI.
So no matter which way you need to send the signal, this should do the trick. Although, it is limited to 1080p (1920×1200) display resolutions.
Remember, if you use an adapter like this, you will only be able to transmit the picture. This is because, unlike HDMI, DVI only supports video signals.
In this case, you would have to send the audio via another connection type like coaxial or optical audio.
If you don’t want to use an adapter, you can buy bi-directional HDMI to DVI cables to send video signals between devices.
- Bi-directional
- Includes the cable
- Available lengths: 3, 6, 10, 15, 25 and 35 feet
- Supports 720p, 1080i and 1080p video
- Video only; audio not supported
The DVI device may also need to be HDCP-enabled to send specific signals like encrypted Blu-ray movies – all HDMI devices support HDCP.
What Are HDMI Right-angle Adapters Used For?
In some situations, you may find it difficult, or even impossible, to plug your HDMI cable into your device.
The most common scenario is where you have your flat screen TV mounted on a wall.
Unless the HDMI ports are on the side of the TV, there will often be no room between the back of the TV and the wall itself to plug in your cable. Oops.
Drum roll, please. Step forward, the life-saving right-angle HDMI adapter!
- Also known as a 90-degree or 270-degree adapter, depending on the orientation
- Pack of two adapters with different orientations
- Works with your existing HDMI cables
- Supports resolutions up to full 4K - 4096x2160 and 3840x2160
- One 270° and one 90° adapter - make sure they will point in the required direction for your requirements
This useful little device will connect to the end of your existing HDMI cable and create a 90-degree connector – thus, allowing you to plug in the cable even in the tightest of areas.
You may also see these described as 270-degree HDMI adapters. It’s the same thing, really. It just means the HDMI connector is designed to point up – rather than down.
If this is important, just make sure you buy one that points the right way.
The adapters linked to above come with both versions – one that points down (90-degree adapter) and another that points up (270-degree adapter).
Of course, this does depend on the orientation of the port on your device.
If you are really on the ball, you can also buy HDMI cables with a right-angle connection already fitted on the end.
- HDMI 90-degree adapter and cable in one
- Available lengths: 3, 6 and 10 feet
- Supports video resolutions up to 4K/60Hz
- 90° orientation: make sure it will connect the way, or you may need a 270° HDMI cable
Therefore, if you don’t have the cables already, you can save on the added expense of buying adapters.
Some people prefer to have a cable with the correct connector hard-wired on the line – rather than use an adapter.
What Does an HDMI Switch Do?
An HDMI switch is helpful if you have run out of HDMI inputs on your projector, monitor, TV or soundbar.
A switch has multiple inputs and an output.
Therefore, you can connect all your devices to the switch and use the single output to connect to your TV.
You can choose which video source to use with a selection button or remote control.
What Is an HDMI Splitter?
A common problem for some people is they want to show a movie on more than one TV screen – or maybe they have a TV and projector and want to run both simultaneously.
This is relatively easy if you play the movie from a device with an HDMI output – like a Blu-ray player or media streamer.
All you need is an HDMI splitter which will send one HDMI output to several destinations. You just need to buy a splitter that has enough outputs.
You also need to make sure that the splitter supports the video resolutions and audio formats that you need.
About The Author
Paul started the Home Cinema Guide to help less-experienced users get the most out of today's audio-visual technology. He has been a sound, lighting and audio-visual engineer for around 20 years. At home, he has spent more time than is probably healthy installing, configuring, testing, de-rigging, fixing, tweaking, re-installing again (and sometimes using) various pieces of hi-fi and home cinema equipment. You can find out more here.















