Are you considering using optical cables to connect your TV, stereo, or home theater setup? You will find optical digital audio connections in many modern AV devices.
I’ve used optical audio many times over the years for sending digital audio to my sound system. It’s a solid choice. But there are others.
In this guide, I’ll give you the lowdown on optical digital audio – how it works, when to use it, and how it stacks up against other options like HDMI and coaxial digital. Read on for all the details.
Key Points
- Optical digital audio cables send uncompressed stereo or compressed 5.1 surround sound between devices using light through optical fiber cables.
- Optical is a good alternative to HDMI for audio when you need to separate audio and video connections or don’t have enough HDMI ports.
- Optical and coaxial digital audio connections offer comparable quality.
- Optical audio converters and switches can solve connectivity problems between devices. For example, converting between optical and coaxial or splitting an optical output to multiple inputs.
Main Topics
The Basics of Optical Digital Audio
An optical digital audio connection sends uncompressed stereo or compressed 5.1 surround sound digital audio between devices using light transmitted through optical fiber cables.
You may also see this connection called a TOSLINK port, named after the developer Toshiba.
Optical digital audio connections are commonly found on the back of TVs to output sound to an external audio system. By connecting this output to an amplifier, you can quickly improve the sound of your television.
Blu-ray players, DVD players, and game consoles also typically have optical outputs to send digital audio to amplifiers, AV receivers, hi-fi DACs (digital-to-analog converters), and soundbars.
Along with HDMI, optical and coaxial are the two primary connection types for sending digital audio.
Both optical and coaxial digital audio are called S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) connections and send the same quality audio.
Here is a selection of popular cables:

- Size: 3 feet to 100 feet
- 24K gold-plated connectors
- Flexible PVC jacket

- Size: 3.3 feet to 15 feet
- Slim braided cable
- Flexible design for easy install

- Size: 3 feet to 20 feet
- Great value
- Ultra-thin cable
What Optical Connectors and Cables Look Like
An optical digital audio connection on your device will look something like this:
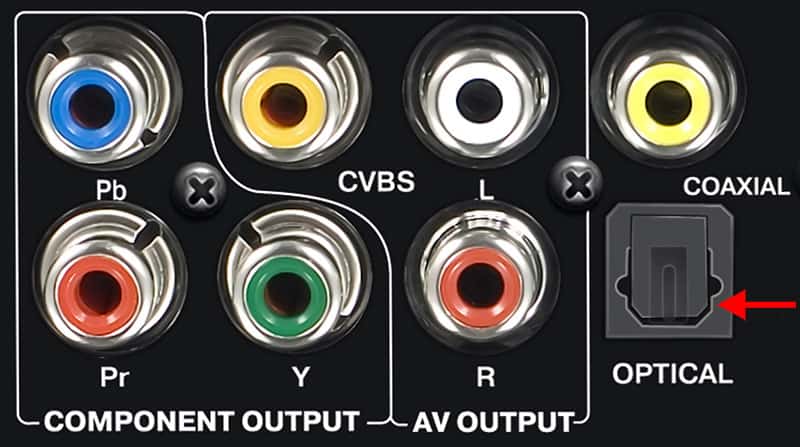

Clue – it’s on the right, hiding above the word optical!
In this example, there is an optical output and a coaxial connection above it – plus some other connections you don’t need to worry about right now.
When connecting two devices, one device will have an optical output. This device sends the sound – like your TV, for example.
The other will have an optical input. This device receives the sound – like your amplifier.
In the picture above, the optical port has a protective ‘door’ that will move out of the way when you push the cable in.
Some optical ports have a protective cap over the hole, which you must remove before you plug in the cable. You can see an example of this below:

When you remove the cap, you will see a bright red light inside the device.
An optical audio cable looks like this:

When you insert the optical cable, it should click into place. It will fit one way only; one side is squared off, with angles on the opposite corners.
If you look carefully, you will see that this matches the shape of the port on your device. So be careful when inserting the cable into your device.
It will click into place quite easily. You don’t need to force it.
Don’t worry too much if some cables have a thicker wire between connectors; this won’t affect the sound.
Optical fiber cables are usually made from inexpensive multimode plastic optical fiber (POF), ideal for short cable runs found in home audio setups. POF is more flexible than glass or silica fibers, making installation easier.
Learn more: Home theater wiring tips and tricks
Which Audio Formats Work With Optical Connections?
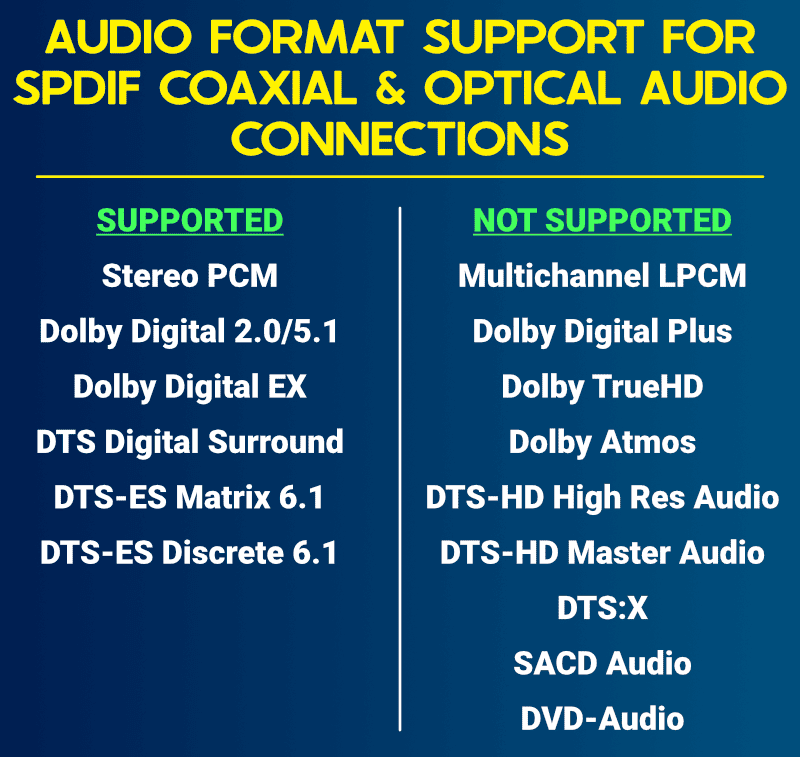
Optical audio connections support the following audio formats:
- Lossless 2.0 (stereo) PCM audio
- Compressed Dolby Digital 2.0/5.1 and Dolby Digital EX
- Compressed DTS Digital Surround, DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 and DTS-ES Discrete 6.1
Due to bandwidth restrictions, optical outputs do not support multichannel LPCM, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby Atmos and DTS:X – or high-definition audio such as Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio.
Optical connections do not support discrete 7.1 soundtracks, as you only find these in unsupported higher-resolution audio formats.
Due to copyright restrictions, optical connections do not support SACD audio and DVD-Audio.
If you try to play unsupported formats on your player via an optical output, the player will usually downmix to stereo. Or play a lower-resolution version of the audio.
The manual for your player will tell you how it will handle unsupported audio formats.
Check out the home theater glossary if you don’t know what these types of audio are.
When Should You Use an Optical Connection?
If your audio/video equipment has HDMI ports, it’s generally best to use HDMI cables for both audio and video signals.
HDMI can transmit all uncompressed stereo and surround sound audio and eliminates the need for a separate audio connection.
However, there are some cases where using an optical audio connection is preferable or necessary:
- Older devices with HDMI may not support audio over HDMI. Optical audio ensures compatibility with those devices.
- For sending your TV’s audio to your sound system. You may be able to use HDMI ARC for this, but many devices don’t have ARC support.
- You may not have enough HDMI ports on a device. Using optical audio for audio frees up the HDMI ports for video-only connections.
- Separating audio and video connections can resolve lip sync issues in some setups.
- Long HDMI cable runs can sometimes cause signal issues, so optical audio provides a reliable separate audio path.
So, while HDMI is ideal for combined audio/video, optical digital audio remains a valuable alternative for specific situations.
How to Connect an Optical Cable From Your TV to Home Theater
Connecting an optical cable from a TV to a home theater system is relatively simple. The basic steps are:
- Remove protective caps from the optical cable, TV optical output and home theater system optical input.
- Connect the cable from the TV’s optical out to the home theater’s optical input – making sure to line up the connector correctly as it will only insert one way around.
- Switch on the TV and amplifier. Ensure the TV’s output is enabled, and you select the correct input on the home theater system.
For more detailed information on this, go to how to connect an optical audio cable to your TV and soundbar.
Problem: Does Your TV’s Optical Output Support 5.1?
A common issue for some people is they can’t get 5.1 surround sound from their TV’s optical output to their sound system or soundbar.
This can be a problem because the optical audio outputs of some TVs don’t pass through a surround sound signal from external devices.
For example, you might have a TV, a DVD player and a soundbar. The DVD player connects to the TV via HDMI, and you send the TV’s audio from the optical output to the soundbar.
So far, so good. But when you hear the DVD’s movie audio on your soundbar system, you only get stereo audio – not 5.1 surround.
The likely reason is that your TV doesn’t support passing through the 5.1 audio from the DVD player to its optical output – and it will only downmix the sound to stereo.
Some TVs will pass through Dolby Digital 5.1 audio and not DTS – or vice versa. Alternatively, others may downmix all external audio to stereo.
If you think this might be a problem, check if the new TV you buy supports 5.1 audio passthrough via optical.
If you already have this problem with your existing equipment, there are a couple of solutions that may work:
- Connect your DVD player directly to the soundbar rather than the TV. This will require your soundbar to support multiple inputs.
- Connect your TV and soundbar using HDMI ARC/eARC rather than optical.
- Use an HDMI audio extractor to split the 5.1 audio from the DVD player’s HDMI output and send the optical signal directly into the soundbar. You may also need an optical audio switch if your soundbar only has one optical input.
- Use an AV receiver and speakers for your surround sound rather than a soundbar. You can then connect the DVD player directly to the receiver.
This article summarizes the 5.1 passthrough support for many new TV models.
This issue will only likely affect audio from external devices, and the audio from streaming apps on the TV itself should pass surround sound OK.
However, if you have an issue with surround sound from an app like Netflix or Disney+, always check your TV’s support for streaming audio via the optical output.
And that the show you are playing does have a 5.1 soundtrack!
What is the Best Optical Cable?
Optical cables for digital audio come in a wide range of lengths, colors – and prices!
You may be tempted to buy the most expensive optical cable because you think it will sound better. But it won’t sound any different.
You won’t get extra special audio by overspending on a cable. Just buy a good value, well-made brand – and note the emphasis on well-made.
Generally, the main differences between cheap and expensive optical cables are:
- Cheap: thinner and more prone to breaking if you regularly reconnect them. Fine for short connections.
- Expensive: thicker, with better shielding, making them more robust for regular rewiring and better for long distances.
But, the thickness of the cable won’t affect performance. They will both sound the same as you are only sending digital audio.
You may see cable manufacturers claim that their optical cables support the transfer of high-resolution audio and Dolby Digital Plus.
While this might be technically true regarding bandwidth, you are unlikely to find many devices supporting these audio formats via their optical connections.
Many choices are available on Amazon, so I would check the reviews and buy one there – or you can support your local AV store.
The AmazonBasics digital optical audio cable should do the job just fine. However, there are other good value brands there too, like this KabelDirekt digital optical audio cable:
- Available lengths: 3, 6, 10,15, 20 and 25 feet
- Premium materials & build quality
- Stereo PCM and compressed 5.1 surround sound
- For game consoles, amplifiers, home theater and TVs
- It doesn't support Dolby Atmos or lossless audio formats - but neither do any other optical cables
Double-check the cable length you are buying and get the right size for your needs.
There’s nothing more annoying than buying a cable and then finding out it’s too short. Been there and done that.
What Is the Maximum Length of an Optical Audio Cable?
A well-made optical audio cable should work well up to 5 meters. You may even get a good signal at 10 meters or more.
However, by the time you get to this length, you are more likely to run into problems. So, consider buying a higher-quality digital optical cable for longer runs.
However, bear in mind that your equipment will also impact this.
The electronics built into your hardware can vary in quality, and you may find that some devices will work over a long cable run – while others won’t. You may just have to try it and see.
Alternatively, you could consider buying a set of optical audio extenders like this:
- Send digital audio up to 300m (990 feet)
- Cat5e or Cat6 Ethernet cables
- Simultaneous output from optical and coaxial
- Free lifetime technical support
- Not for connecting to a computer network - for the transfer of digital audio only
These extenders use Cat5 or Cat6 cables to send the optical audio signal long distances.
They work up to a distance of 300 meters and also support coaxial audio connections.
Optical vs HDMI: Which Is Better?
Should you use optical or HDMI for your audio connections?
Firstly, do they sound different? No, they don’t.
If you are sending the same audio format, it will sound the same regardless of whether you are using optical or HDMI.
The main advantage of HDMI over an optical connection is that HDMI supports more audio formats.
Optical and HDMI both support uncompressed stereo and 5.1 Dolby Digital and DTS audio.
However, HDMI also supports Dolby Digital Plus and high-resolution audio like Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, Dolby Atmos and DTS:X.
Also, HDMI has the advantage of HDMI ARC and eARC connections, where you can send audio from a TV to a soundbar or AV receiver.
This can sometimes save you from installing an extra cable in your system.
Here is a handy table comparing the differences between optical and HDMI ARC and HDMI eARC connections:
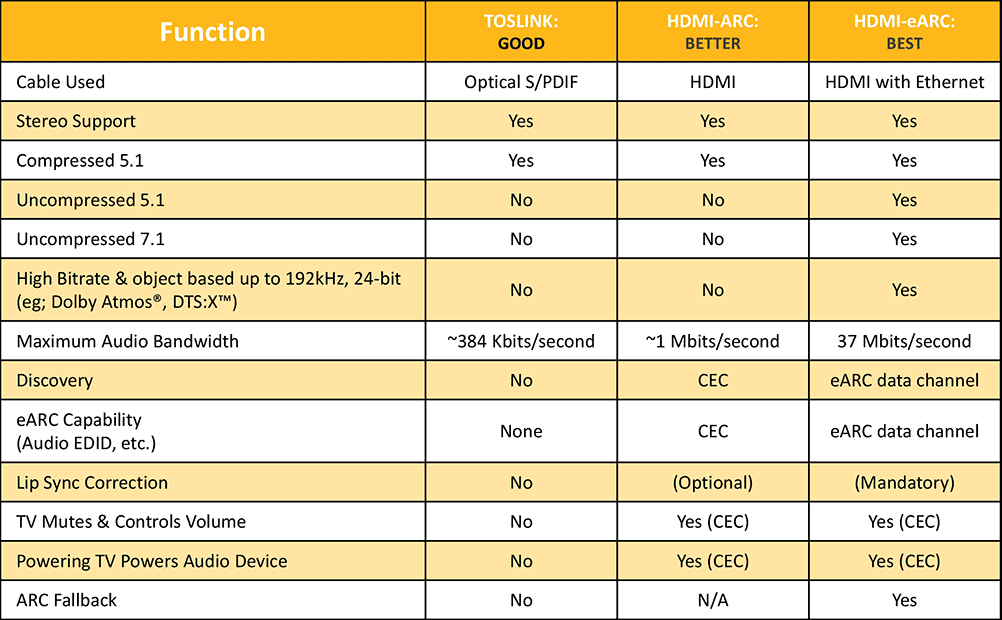
Source: HDMI.org
The bottom line? HDMI supports more audio formats and might save you an extra cable if your system supports ARC or eARC.
However, an optical connection will sound just as good as HDMI if you don’t need anything more than stereo or compressed 5.1 surround sound.
Optical or Coaxial: Picking the Best Type
Optical and coaxial offer comparable audio quality for the same audio format – and both send S/PDIF digital audio signals.
TOSLINK connections were initially designed to run to a maximum of 48 kHz. However, many newer devices increased the supported resolution to 24/96.
This is commonly thought to be the maximum resolution of optical audio – although there is a question of why many devices don’t support higher resolutions.
Coaxial connections commonly support 24/192 resolution audio, so higher resolution audio formats may be one reason to choose coaxial over optical audio.
A potential benefit of optical connections is that they won’t be affected by electromagnetic interference. In theory, coaxial could be.
Another consideration is that the sound quality may vary by device. Before you hear a digital audio signal, you must convert it to analog audio.
A DAC performs this process, so a poorly designed device may create audible differences when using optical or coaxial inputs. In contrast, a high-quality device shouldn’t sound any different.
The sound quality of optical and coaxial connections in the real world will be similar – and the one you choose will usually depend on your devices’ connections or the cables you have available.
How to Convert Digital Optical Audio to RCA Coaxial
Sometimes, you can use an audio converter to solve problems passing audio between devices.
For example, you might have an optical output on your Blu-ray player but wish to send audio directly into your amplifier – which only has a coaxial digital audio input.
However, there is a simple solution. You can buy an optical audio converter to change the audio to an RCA coaxial output, like the one pictured below:
- Use it if you don't have the correct digital audio connections on your device
- Bi-directional so you can convert both ways
- Supports uncompressed stereo PCM audio and 5.1 Dolby Digital and DTS
- Works up to 30 meters
- Power connection required
This will take an optical output and output the audio signal via coaxial. Terrific!
The one highlighted above is bi-directional, meaning you can also use it to convert a coaxial output to an optical input. This is useful in some situations.
Converters can solve many problems when mixing and matching different audio types and connections. You just need to ensure the converter will pass all the signals you want.
For example, some may only send stereo audio, not multichannel surround sound. The one above supports both.
Converting Optical to Stereo Analog Audio
Another common problem is you want to send optical audio to an old analog amplifier with no digital inputs.
The solution is to buy a digital optical to analog RCA audio adapter, which converts the digital audio to stereo analog audio.
You can see an example of one pictured below:
- Optical and coaxial digital audio inputs
- Accepts PCM and Dolby/DTS 5.1 input audio
- 192/24 lossless decoding
- Output volume control
- Only outputs stereo analog audio, not surround sound.
This device will accept an optical or coaxial digital audio connection and output the audio as stereo analog.
For more details on these converters, look at how to convert optical audio to RCA stereo.
How to Convert Analog RCA to Digital Optical Audio
In the previous example, you learned how to convert digital to analog audio. However, what if you needed to convert the audio the other way? From analog to digital.
An example might be when you have a device like an old tape deck – and want to send the audio to the optical input of an amplifier or soundbar.
You can do that with a converter like this:
- Supports uncompressed 2-channel PCM/LPCM stereo audio
- Converts to S/PDIF coaxial or TOSLINK optical audio
- Sampling rate: 48 kHz
- Not bi-directional - analog to digital only.
The above device also converts to a coaxial output as well as optical.
Before buying any converters like these, always make sure you know the audio output and input format. If you get a device that converts the wrong way, it won’t work.
What Is an Optical Audio Switch Used For?
Another potential issue you may come across is that you have a limited number of optical inputs on your AV receiver or soundbar.
In this scenario, if you have two or three devices that you want to connect to your amplifier via an optical connection, then you can buy an optical audio switch, like the one pictured below:
- 3-into-1 optical connection
- For any devices with an optical out like TV, Blu-ray player, cable box or game console
- Works up to 40 meters
- Remote control included
- You can only use one input device at a time
This little box of tricks will accept the optical audio outputs of up to three devices and output them into a single input on your amplifier.
The model above has a remote control to switch between audio inputs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does an Optical Audio Cable Send Video?
No, the optical connection on your AV device is for digital audio only.
What Is a TOSLINK Cable?
A TOSLINK cable is another name for an optical audio cable. The digital optical audio connection type was created by Toshiba, which is where the term originates. Most people refer to this connection as optical audio, but you may see the connection or cable called TOSLINK occasionally.
Does Optical or TOSLINK Support 5.1 Audio?
Yes, optical audio connections support compressed Dolby Digital or DTS 5.1 surround sound.
Can You Send Dolby Digital Plus Over Optical?
No. Optical audio connections only support PCM stereo or compressed 5.1 Dolby Digital or DTS audio. Some devices may play a lower-resolution version of Dolby Digital Plus via optical. But, most will downmix the audio to stereo.
Does Dolby Atmos Work With an Optical Cable?
No. Dolby Atmos is only available with Dolby Digital Plus or high-resolution Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD Master Audio soundtracks. These formats require too much bandwidth for an optical connection.
What Does Digital Audio Out Mean?
A digital audio out refers to an audio output on a TV, Blu-ray player, game console – or any other AV device that creates sound. This output will send stereo or 5.1 surround sound audio to an amplifier, home theater system or soundbar. There are two main types of digital audio out – optical and coaxial.
About The Author
Paul started the Home Cinema Guide to help less-experienced users get the most out of today's audio-visual technology. He has been a sound, lighting and audio-visual engineer for around 20 years. At home, he has spent more time than is probably healthy installing, configuring, testing, de-rigging, fixing, tweaking, re-installing again (and sometimes using) various pieces of hi-fi and home cinema equipment. You can find out more here.










